Abstract
Background: Sickle cell patients produce more reactive oxygen species (ROS) than healthy individuals, leading to increased cell membrane damage. Theoretically, reducing ROS formation would preserve red cell membranes of sickle cell patients. Vitamin C is a powerful anti-oxidant capable of inhibiting ROS formation in a variety of situations, by functioning as an electron donor to reduce molecular oxygen. This study aimed to determine whether Vitamin C reduced ROS formation in sickle red cells.
Methods: 27 homozygous (HbSS) patients were recruited from the outpatient clinics of Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Nigeria, and annex at the Sickle Cell Foundation, Lagos, Nigeria. Demographic information and EDTA patient blood samples were collected. The test group were red cells preincubated in 80uM and 100uM Vitamin C concentrations before stressing with tertbutylhydroperoxide. These were compared to stressed matched controls preincubated in phosphate buffered saline. Cell staining was done with CellRox Orange followed by flow cytometry to quantify ROS.
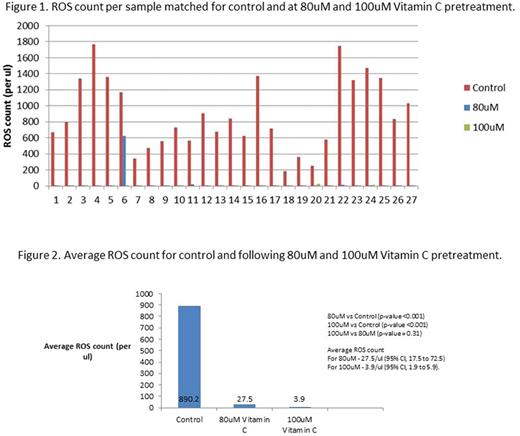
Results: ROS count for Vitamin C pre-treated red cells was significantly lower than matched controls (p<0.001). Average ROS count for 80uM test samples was 27.5/ul (95% CI, 17.5 to 72.5) and for 100uM 3.9/ul (95% CI, 1.9 to 5.9). Male gender was significantly associated with elevated baseline ROS count (p=0.03).
Conclusion: Vitamin C reduced ROS formation in HbSS cells. Future studies should focus on a role for Vitamin C as a safe, cheap addition to maintenance therapy of sickle cell patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal